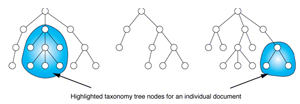
During the analysis of a document, all nodes
in the taxonomy tree that are addressed by the text-analysis
process are highlighted, and the ensemble of highlighted nodes indicates
the thematic areas covered by the document.
The corresponding thematic areas of each document are then
projected into a 100-dimensional content-space, and finally, a categorization
of the documents is achieved by means of a self-organizing neural network
(Kohonen-Map), ending up with the documents grouped in "well-organized
bookshelves." The neural network also provides a scientifically
founded similarity measure based
on information-theoretical principals that allow the comparison of documents
according to their content.
This content recognition and categorization technology works
across several different languages, recognizing, for example, that an
English translation of a French, German, Italian, or Spanish document
has the same content and contains the same information as the original
document.
Unlike other systems, categorization with InfoCodex functions
automatically, without any user intervention. This function eliminates
the cumbersome and costly training for documentation classification
- a significant advantage.